Volume meaning in science is more than just a term; it’s a fundamental concept that shapes how we understand space, matter, and measurements. Imagine filling up a container with water or calculating how much space an object occupies. That’s where volume comes into play. Whether you're a student, a scientist, or simply curious about the world around you, understanding volume is essential. In this article, we'll dive deep into what volume really means in the scientific context, breaking it down step by step so you can grasp the concept like a pro.
When you hear the word "volume," your mind might jump to loudness or music levels, but in science, it’s all about the amount of three-dimensional space an object occupies. This concept is crucial in fields like physics, chemistry, and engineering. From measuring liquids to calculating the density of materials, volume plays a key role in scientific research and everyday life.
So, why is understanding volume so important? Well, it’s not just about numbers; it’s about comprehending how things fit together, how substances interact, and how we measure the world around us. Whether you're designing a building, mixing chemicals, or even baking a cake, knowing the volume of ingredients or materials is vital. Stick with me as we unravel the mysteries of volume meaning in science.
Read also:King Henry Viiis Wives The Untold Stories Of Love Power And Betrayal
What is Volume Meaning in Science?
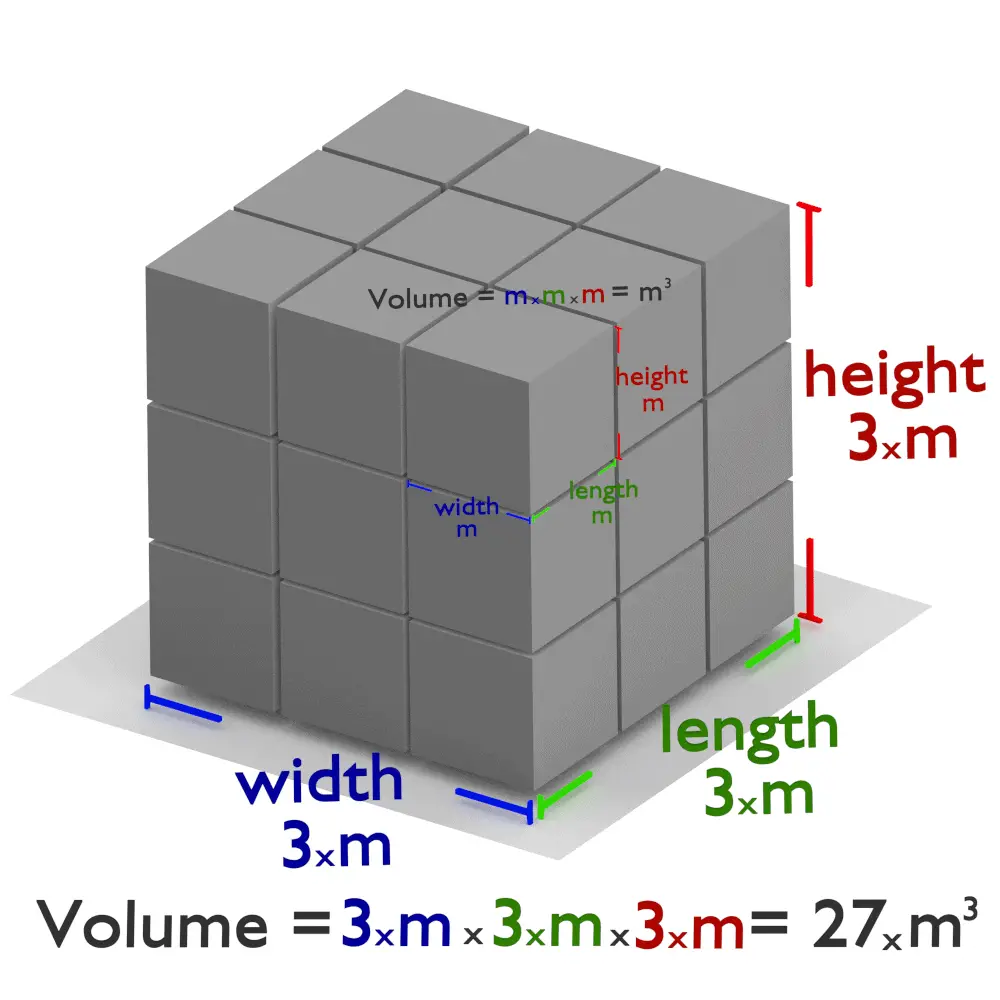
Let’s start with the basics. In scientific terms, volume refers to the amount of three-dimensional space an object or substance occupies. It’s a fundamental property of matter that helps us understand how much space something takes up. Think of it like this: if you have a box, the volume is the total space inside that box where you can store stuff. Simple, right? But there’s more to it than meets the eye.
Volume is typically measured in cubic units, such as cubic centimeters (cm³) or liters (L). These units help us quantify the space an object occupies, making it easier to compare and analyze different substances. For example, when you fill a glass with water, the volume of the water is the amount of space it takes up inside the glass.
Key Characteristics of Volume
Here are some important points to remember about volume:
- Volume is a scalar quantity, meaning it has magnitude but no direction.
- It applies to solids, liquids, and gases, although the methods for measuring volume may vary depending on the state of matter.
- Volume is closely related to other properties like density and mass, which we’ll explore later in this article.
How to Measure Volume in Science
Measuring volume is a crucial skill in science, and there are several methods to do it depending on the type of substance you’re dealing with. For solids, you can use geometric formulas to calculate volume based on shape. For liquids and gases, you’ll need specialized tools like graduated cylinders or displacement methods.
Measuring Volume for Solids
If you’re working with regular-shaped solids like cubes or spheres, you can use mathematical formulas to calculate their volume. For example:
- Cube: Volume = side³
- Sphere: Volume = (4/3)πr³
But what about irregularly shaped objects? That’s where the water displacement method comes in. By submerging the object in water and measuring the amount of water displaced, you can determine its volume. Cool, right?
Read also:Matthew Gray Gubler Wife Everything You Need To Know About His Love Life
Measuring Volume for Liquids
For liquids, the easiest way to measure volume is by using a graduated cylinder. Simply pour the liquid into the cylinder and read the measurement at the bottom of the meniscus (the curved surface of the liquid). This method is accurate and widely used in labs around the world.
Volume Meaning in Different States of Matter
Volume behaves differently depending on the state of matter. Let’s take a closer look at how it applies to solids, liquids, and gases.
Volume in Solids
Solids have a fixed shape and volume, which makes them easier to measure. However, irregularly shaped solids require creative methods like water displacement to determine their exact volume. Solids are also less compressible, meaning their volume doesn’t change much under pressure.
Volume in Liquids
Liquids take the shape of their container but maintain a constant volume. This makes them ideal for measuring using tools like graduated cylinders or beakers. Liquids are slightly compressible, but the change in volume under pressure is usually negligible.
Volume in Gases
Gases are highly compressible and expand to fill the volume of their container. This means that the volume of a gas depends on factors like temperature and pressure. Scientists often use the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) to calculate the volume of gases under different conditions.
Volume and Its Relationship with Other Properties
Volume doesn’t exist in isolation; it’s closely linked to other properties like density and mass. Understanding these relationships is key to mastering the concept of volume in science.
Volume and Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume. This means that to calculate density, you need to know both the mass and the volume of a substance. The formula is simple: Density = Mass/Volume. For example, if you have a block of wood with a mass of 10 grams and a volume of 5 cm³, its density would be 2 grams per cm³.
Volume and Mass
Mass refers to the amount of matter in an object, while volume measures the space it occupies. These two properties are often used together to calculate density or to compare different substances. For instance, a small object can have a high mass if it’s made of a dense material, while a large object might have a low mass if it’s made of a less dense material.
Applications of Volume in Science
Volume isn’t just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various fields of science. From engineering to medicine, understanding volume is essential for solving real-world problems.
Volume in Chemistry
In chemistry, volume is used to measure the amount of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. It’s also crucial for calculating concentrations and determining the molar volume of gases. Chemists often use tools like pipettes and burettes to measure small volumes with precision.
Volume in Physics
Physics relies heavily on volume to study phenomena like pressure, buoyancy, and fluid dynamics. For example, Archimedes’ principle explains how the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by its volume. This principle is used in everything from shipbuilding to weather forecasting.
Volume in Engineering
Engineers use volume to design structures, calculate material requirements, and optimize performance. Whether it’s determining the capacity of a water tank or designing the aerodynamics of an airplane, volume plays a critical role in engineering projects.
Common Misconceptions About Volume
Even though volume is a fundamental concept, there are still some common misconceptions floating around. Let’s clear them up!
Volume vs. Capacity
Many people confuse volume with capacity, but they’re not the same thing. Volume refers to the amount of space an object occupies, while capacity refers to the amount of substance a container can hold. For example, a bottle may have a volume of 500 cm³, but its capacity might be 400 mL if it’s not completely filled.
Volume and Shape
Some people think that objects with irregular shapes can’t have a defined volume, but that’s not true. As we discussed earlier, methods like water displacement allow us to measure the volume of irregularly shaped objects accurately.
Fun Facts About Volume
Here are some interesting tidbits about volume that might surprise you:
- The largest known star, UY Scuti, has a volume so massive that it could fit over 5 billion suns inside it!
- Humans are made up of about 60% water, which means our bodies have a significant volume of liquid.
- The concept of volume has been studied since ancient times, with early civilizations using it to build pyramids and aqueducts.
Conclusion: Why Volume Matters in Science
In conclusion, understanding volume meaning in science is crucial for anyone interested in the natural world. From measuring liquids to calculating the density of materials, volume plays a vital role in scientific research and everyday life. By mastering this concept, you’ll be better equipped to tackle complex problems and gain a deeper appreciation for the world around you.
So, what’s next? If you found this article helpful, why not share it with your friends or leave a comment below? Let’s keep the conversation going and explore more fascinating topics in science. Who knows? You might just discover your next passion!
Table of Contents