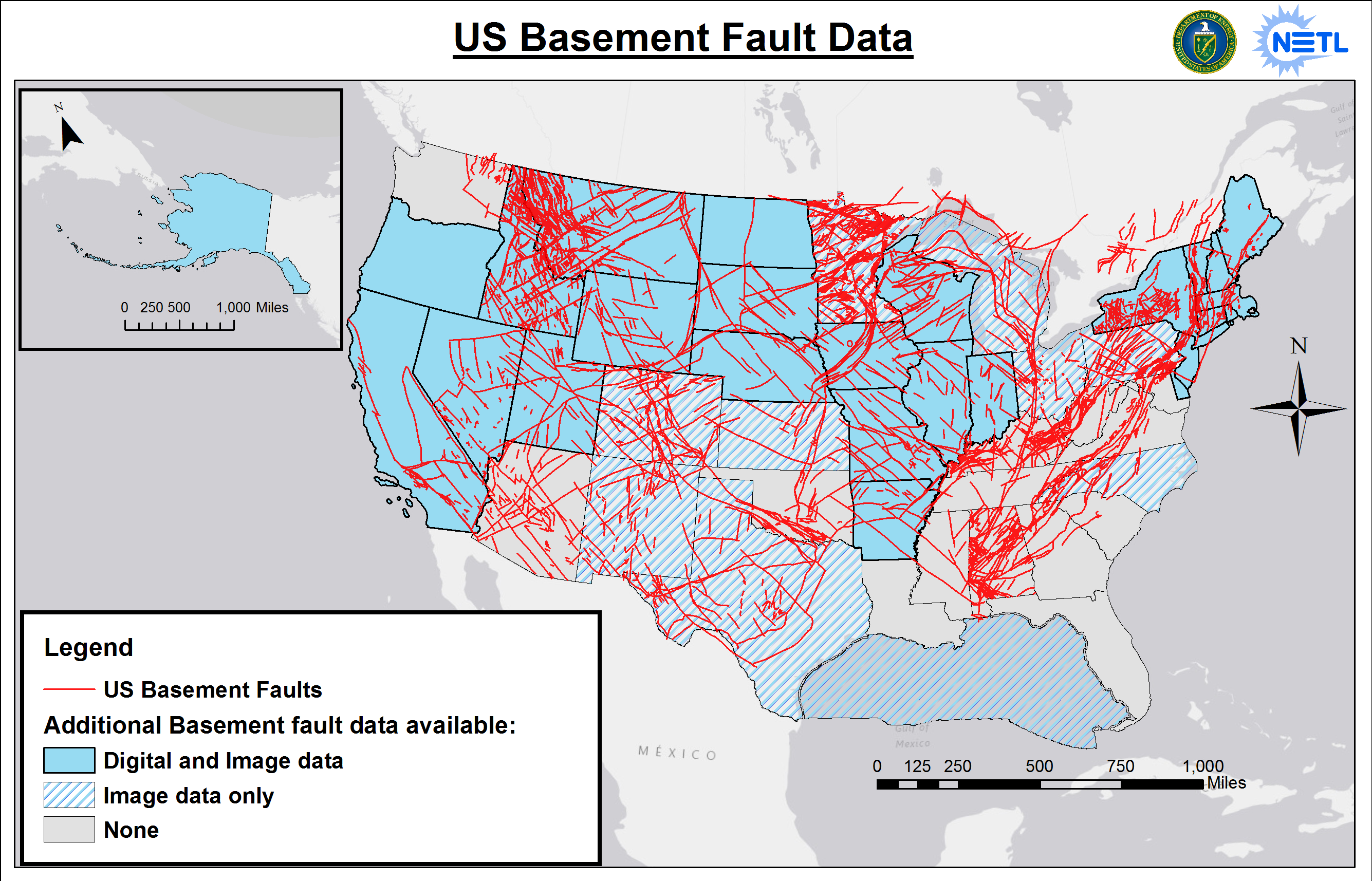
Ever wondered what those wavy lines on a map really mean? Fault lines on a map are more than just random squiggles; they’re the planet’s version of stretch marks from all the tectonic drama happening beneath our feet. These lines reveal the hidden fractures in Earth’s crust where massive plates meet, grind, and sometimes violently collide. Understanding fault lines is key to predicting earthquakes, shaping urban planning, and even uncovering geological mysteries that have puzzled scientists for decades.
Picture this: Earth’s crust isn’t one solid piece but more like a giant jigsaw puzzle made up of massive plates floating on molten rock. When these plates move, they don’t always play nice—sometimes they crash, slip, or get stuck. That’s where fault lines come in, marking the battlegrounds of these geological battles. If you’ve ever felt the ground shake, chances are a fault line nearby was flexing its muscles.
But here’s the thing: fault lines aren’t just scientific curiosities. They’re living, breathing (well, sort of) parts of our planet that affect everything from where we build cities to how we prepare for natural disasters. So, buckle up as we dive deep into the world of fault lines, uncovering their secrets and learning why they matter so much to us.
Read also:Will Douglas And Kaitlan Collins A Deep Dive Into Their World
Table of Contents
- What Are Fault Lines?
- Types of Fault Lines
- How Fault Lines Appear on a Map
- Famous Fault Lines Around the World
- The Impact of Fault Lines on Human Life
- Earthquake Preparedness Near Fault Lines
- Scientific Research on Fault Lines
- Geological Significance of Fault Lines
- Urban Planning Around Fault Lines
- Conclusion
What Are Fault Lines?
Let’s start with the basics. Fault lines are essentially cracks in the Earth’s crust where tectonic plates meet. Think of them as the seams in a giant puzzle that occasionally don’t fit perfectly. These cracks occur because the plates are constantly moving—sometimes sliding past each other, sometimes colliding head-on, and sometimes pulling apart.
Now, here’s the kicker: fault lines aren’t just static features. They’re active zones where energy builds up over time and is eventually released in the form of earthquakes. In fact, most of the world’s earthquakes occur along fault lines, making them both fascinating and potentially dangerous.
How Fault Lines Form
So, how do these cracks form in the first place? Well, it all comes down to plate tectonics. The Earth’s crust is divided into several large and small plates that float on the semi-fluid mantle below. When these plates move, they create stress in the crust. If the stress becomes too much, the crust breaks, forming a fault line.
- Convergent boundaries: Where plates collide, pushing the crust upward and sometimes causing mountains to form.
- Divergent boundaries: Where plates pull apart, creating new crust as magma rises to fill the gap.
- Transform boundaries: Where plates slide past each other, often causing earthquakes.
Types of Fault Lines
Not all fault lines are created equal. Depending on how the plates interact, fault lines can take on different forms, each with its own set of characteristics. Let’s break them down:
Normal Faults
These occur when the Earth’s crust stretches and thins, causing one block of rock to slide down relative to the other. Picture a cliff face where the top part has slid downward.
Reverse Faults
In contrast to normal faults, reverse faults happen when the crust is compressed, pushing one block of rock upward. This often leads to the formation of mountains.
Read also:Victoria Ruffo The Iconic Talent Who Lit Up Mexican Television
Strike-Slip Faults
These are the ones where plates slide past each other horizontally. The San Andreas Fault in California is a famous example of a strike-slip fault.
How Fault Lines Appear on a Map
When you look at a geological map, fault lines are usually represented by wavy or straight lines with symbols indicating the type of fault. These maps are like treasure maps for geologists, revealing the hidden structure of the Earth’s crust.
But here’s the thing: not all fault lines are visible on the surface. Some are buried deep underground, only detectable through advanced imaging techniques. This makes mapping fault lines a complex and ongoing process.
Tools Used to Map Fault Lines
Geologists use a variety of tools to map fault lines, including:
- Seismic surveys: Detecting underground faults by analyzing earthquake waves.
- Satellite imagery: Identifying surface features that indicate fault lines.
- Drilling: Collecting rock samples to study fault zones up close.
Famous Fault Lines Around the World
Some fault lines are so famous they’ve become household names. Let’s take a look at a few of the most notable ones:
The San Andreas Fault
Stretching over 800 miles through California, the San Andreas Fault is one of the most well-known fault lines in the world. It’s responsible for some of the largest earthquakes in recorded history and continues to pose a significant threat to the region.
The Alpine Fault
Located in New Zealand, the Alpine Fault is another major fault line that has produced powerful earthquakes. Scientists believe it’s overdue for a significant event, making it a focus of intense study and monitoring.
The Impact of Fault Lines on Human Life
Fault lines don’t just affect the natural landscape; they have a profound impact on human life as well. From influencing where we live to shaping our infrastructure, fault lines play a crucial role in our daily lives.
Urban Planning Challenges
Building near fault lines presents unique challenges. Engineers and architects must design structures that can withstand the forces of earthquakes, while city planners must consider evacuation routes and emergency response plans.
Economic Consequences
Earthquakes caused by fault lines can have devastating economic impacts, destroying infrastructure, disrupting supply chains, and causing billions in damages. This makes understanding and preparing for fault line activity a top priority for governments and businesses alike.
Earthquake Preparedness Near Fault Lines
Living near a fault line doesn’t have to be a recipe for disaster. With proper preparation, communities can minimize the risks associated with earthquakes. Here are a few tips:
- Build earthquake-resistant structures.
- Develop emergency response plans.
- Conduct regular earthquake drills.
- Stay informed about fault line activity in your area.
Scientific Research on Fault Lines
Scientists are constantly studying fault lines to better understand their behavior and predict earthquakes. This research involves a combination of fieldwork, laboratory experiments, and advanced modeling techniques.
Key Findings
Recent studies have revealed new insights into fault line mechanics, such as the role of fluid pressure in triggering earthquakes and the potential for fault lines to interact with each other in complex ways.
Geological Significance of Fault Lines
Beyond their role in earthquakes, fault lines are also crucial to understanding the Earth’s geological history. They provide a window into the processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
Fossilized Faults
Some fault lines that were once active are now fossilized, offering valuable information about past geological events. By studying these ancient faults, scientists can piece together the story of Earth’s dynamic past.
Urban Planning Around Fault Lines
As cities continue to grow, the challenge of building near fault lines becomes increasingly important. Urban planners must balance the need for development with the risks posed by fault line activity.
Innovative Solutions
From designing flexible buildings to creating open spaces that can serve as emergency zones, urban planners are coming up with creative solutions to mitigate the risks of fault line proximity.
Conclusion
Fault lines on a map may seem like just a bunch of lines, but they’re so much more than that. They’re the keys to understanding our planet’s dynamic nature and the forces that shape our world. Whether you’re a scientist, an urban planner, or just someone curious about the Earth beneath your feet, fault lines offer a fascinating glimpse into the inner workings of our planet.
So, the next time you see those squiggly lines on a map, remember that they’re not just random marks. They’re the scars of a restless Earth, reminding us of the power and unpredictability of nature. And if you live near a fault line, take the time to prepare—because when it comes to earthquakes, knowledge really is power.
Now, it’s your turn. Share your thoughts on fault lines in the comments below, or check out some of our other articles on geology and natural disasters. Stay curious, stay safe, and keep exploring!