De facto segregation is a term that describes separation based on race, ethnicity, or other factors without explicit legal enforcement. It’s not something you see written in laws or official documents, but it’s very real in how it shapes communities and opportunities. This type of segregation occurs because of social, economic, and historical factors rather than government mandates. Let’s dive into why it matters, how it happens, and what we can do about it.
When you think of segregation, you might picture Jim Crow laws or apartheid systems—things that were officially enforced by governments. But de facto segregation is different. It’s like a shadow system, quietly influencing where people live, work, and go to school without anyone saying it’s the law. It’s a complex web of factors, and understanding it means looking beyond the surface.
This article will explore the definition of de facto segregation, its causes, effects, and potential solutions. Whether you’re a student, educator, or just someone curious about how society works, this topic affects us all. So grab your favorite drink, and let’s break it down together. Trust me, it’s worth the read.
Read also:King Henry Viiis Wives The Untold Stories Of Love Power And Betrayal
Table of Contents
- What is De Facto Segregation?
- A Brief History of Segregation
- The Causes Behind De Facto Segregation
- Economic Factors Driving Segregation
- Housing Policies and Their Role
- Impact on Education Systems
- Possible Solutions to Combat Segregation
- Key Statistics and Data
- Challenges in Addressing the Issue
- Final Thoughts and Call to Action
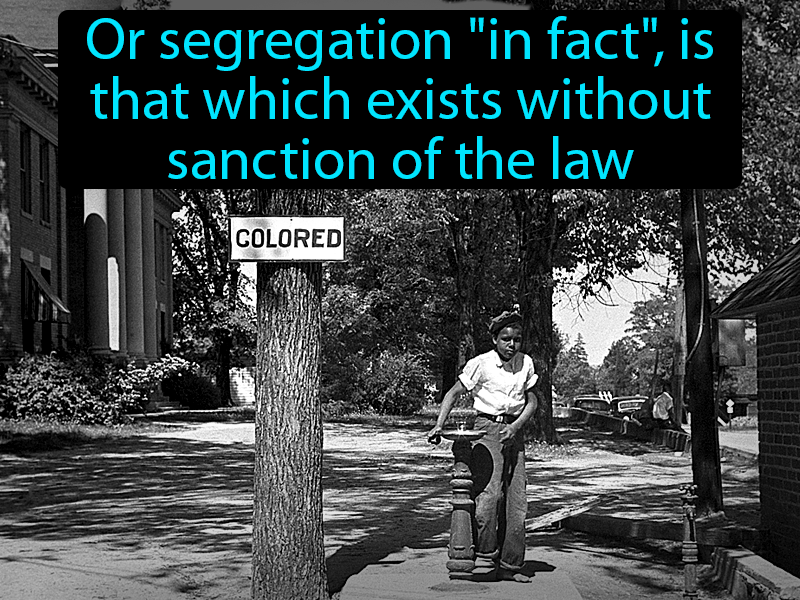
What is De Facto Segregation?
De facto segregation refers to the separation of groups based on race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status without any legal mandate. Unlike de jure segregation, which is enforced by law, de facto segregation arises from societal norms, economic disparities, and historical patterns. Think of it as the invisible hand guiding where people settle, work, and send their kids to school.
This type of segregation is often subtle, yet its impact is profound. For example, neighborhoods with predominantly Black or Hispanic residents may have fewer resources compared to predominantly white areas. It’s not because it’s illegal for them to live elsewhere; it’s because systemic barriers make it harder for them to do so.
Why Does De Facto Segregation Matter?
Here’s the thing: segregation affects more than just where you live. It impacts access to quality education, healthcare, employment opportunities, and even social mobility. People living in segregated areas often face challenges that those in more integrated communities don’t. It’s a cycle that perpetuates inequality, and understanding it is the first step toward change.
A Brief History of Segregation
To truly grasp de facto segregation, we need to look back at its roots. Historically, segregation was often codified into law, especially in the United States during the Jim Crow era. But even after those laws were abolished, the effects didn’t just disappear overnight. Redlining, discriminatory lending practices, and restrictive covenants continued to shape neighborhoods long after segregation was declared illegal.
Redlining, for instance, was a practice where banks refused to lend money to people in certain neighborhoods—often minority communities. This created cycles of poverty and limited opportunities for homeownership and wealth accumulation. Over time, these practices contributed to the de facto segregation we see today.
How History Shapes Modern-Day Segregation
The legacy of past policies lingers, influencing everything from housing markets to school districts. Even though laws have changed, the patterns they created persist. For example, many urban areas still reflect the racial and economic divisions established decades ago. It’s like trying to erase a stain—it doesn’t happen overnight.
Read also:Oregon Ducks Basketball Roster Your Ultimate Guide To The Ducks Lineup
The Causes Behind De Facto Segregation
So, how does de facto segregation happen? It’s a mix of several factors working together. Economic inequality, housing policies, and social attitudes all play a role. Let’s break it down:
- Economic Disparities: Wealthier families can afford to live in better neighborhoods, while lower-income families are often restricted to areas with fewer resources.
- Housing Policies: Practices like redlining and zoning laws have historically limited where certain groups can live.
- Social Attitudes: Stereotypes and biases can influence where people choose to settle, creating self-segregated communities.
It’s not just one factor; it’s a combination of all these things working together to create a system that perpetuates division.
Understanding the Root Causes
To tackle de facto segregation, we need to address its root causes. That means looking at how economic policies, housing regulations, and social norms contribute to the problem. It’s not enough to say, “We should all get along.” We need actionable steps to dismantle the systems that keep people apart.
Economic Factors Driving Segregation
Money talks, and when it comes to segregation, it often whispers loud enough to shape entire communities. Economic inequality is a major driver of de facto segregation. Families with higher incomes can afford to live in neighborhoods with better schools, parks, and infrastructure. Meanwhile, lower-income families are often left with fewer options.
This disparity isn’t just about individual choices; it’s about systemic barriers. For example, neighborhoods with predominantly minority residents often receive less investment, leading to declining property values and fewer amenities. It’s a vicious cycle that’s hard to break.
How Economic Disparities Affect Communities
The effects of economic inequality go beyond just where people live. They influence everything from health outcomes to educational attainment. Children growing up in low-income, segregated neighborhoods often face additional challenges, such as overcrowded classrooms and limited access to extracurricular activities. It’s not just about money—it’s about opportunity.
Housing Policies and Their Role
Housing policies have played a significant role in shaping de facto segregation. Practices like redlining, exclusionary zoning, and discriminatory lending have all contributed to the separation of communities. These policies may not exist in the same form today, but their effects are still felt.
For example, zoning laws that restrict the construction of affordable housing in certain areas effectively keep lower-income families out. It’s like putting up an invisible wall around neighborhoods, saying, “You don’t belong here.”
Reforming Housing Policies for Equality
Addressing de facto segregation requires rethinking housing policies. That means promoting inclusive zoning, increasing access to affordable housing, and eliminating discriminatory practices. It’s not an easy fix, but it’s a necessary one if we want to create truly integrated communities.
Impact on Education Systems
One of the most significant impacts of de facto segregation is on education. Schools in segregated neighborhoods often face challenges that more integrated schools don’t. They may have fewer resources, higher teacher turnover rates, and larger class sizes. This creates a gap in educational quality that’s hard to close.
Research shows that students in racially and economically diverse schools tend to perform better academically and socially. Yet, many schools remain segregated due to housing patterns and district boundaries. It’s a Catch-22 that needs addressing.
Promoting Educational Equity
To combat the effects of de facto segregation in education, we need policies that promote diversity and equity. That could mean redrawing school district lines, providing additional resources to underfunded schools, or implementing magnet programs that attract students from different backgrounds. It’s about giving every child a fair shot at success.
Possible Solutions to Combat Segregation
Now that we’ve talked about the problem, let’s focus on the solutions. Addressing de facto segregation requires a multi-faceted approach. Here are a few ideas:
- Promote Affordable Housing: Increase the availability of affordable housing in diverse neighborhoods to encourage integration.
- Reform Zoning Laws: Eliminate exclusionary zoning practices that restrict where people can live.
- Invest in Education: Provide additional funding and resources to schools in segregated areas.
- Foster Community Engagement: Encourage dialogue and collaboration between different groups to break down barriers.
It’s not just about policies; it’s about people working together to create change.
Implementing Change at the Local Level
Local governments and communities have a crucial role to play in addressing de facto segregation. By implementing policies that promote diversity and inclusion, they can make a real difference. It’s about taking small steps that add up to big changes over time.
Key Statistics and Data
Numbers don’t lie, and when it comes to de facto segregation, the statistics tell a powerful story. Here are a few key points:
- In 2020, the average Black family earned only 59% of what the average white family earned.
- Minority neighborhoods often receive 25% less investment than predominantly white areas.
- Schools in high-poverty areas spend about $1,000 less per student annually compared to wealthier districts.
These numbers highlight the disparities that exist and underscore the need for action.
Data-Driven Approaches to Segregation
Using data to inform policy decisions is essential. By analyzing trends and identifying areas of need, we can target resources more effectively. It’s about making smart, evidence-based choices that drive real change.
Challenges in Addressing the Issue
Addressing de facto segregation isn’t easy. There are plenty of challenges, from political resistance to social attitudes. Some people may not even realize the extent of the problem or its impact on their communities. Overcoming these obstacles requires persistence and collaboration.
Another challenge is ensuring that solutions don’t inadvertently create new problems. For example, gentrification can lead to displacement, which may worsen segregation in other areas. It’s a delicate balance that requires careful consideration.
Building Bridges, Not Walls
The key to overcoming these challenges is building bridges between different groups. That means fostering understanding, promoting dialogue, and working together toward common goals. It’s about creating a society where everyone has a seat at the table.
Final Thoughts and Call to Action
De facto segregation is a complex issue with deep roots in history and society. But it’s not insurmountable. By understanding its causes, effects, and potential solutions, we can take steps toward a more equitable future. Whether it’s through policy changes, community engagement, or individual actions, we all have a role to play.
So here’s my call to action: Don’t just sit there. Get involved. Talk to your neighbors, attend local meetings, and advocate for policies that promote diversity and inclusion. Together, we can make a difference. Share this article, leave a comment, and let’s keep the conversation going. The more we talk about it, the closer we get to change.

/GettyImages-108489277-b803664f7e5548e38b5d2846321e0dfe.jpg)