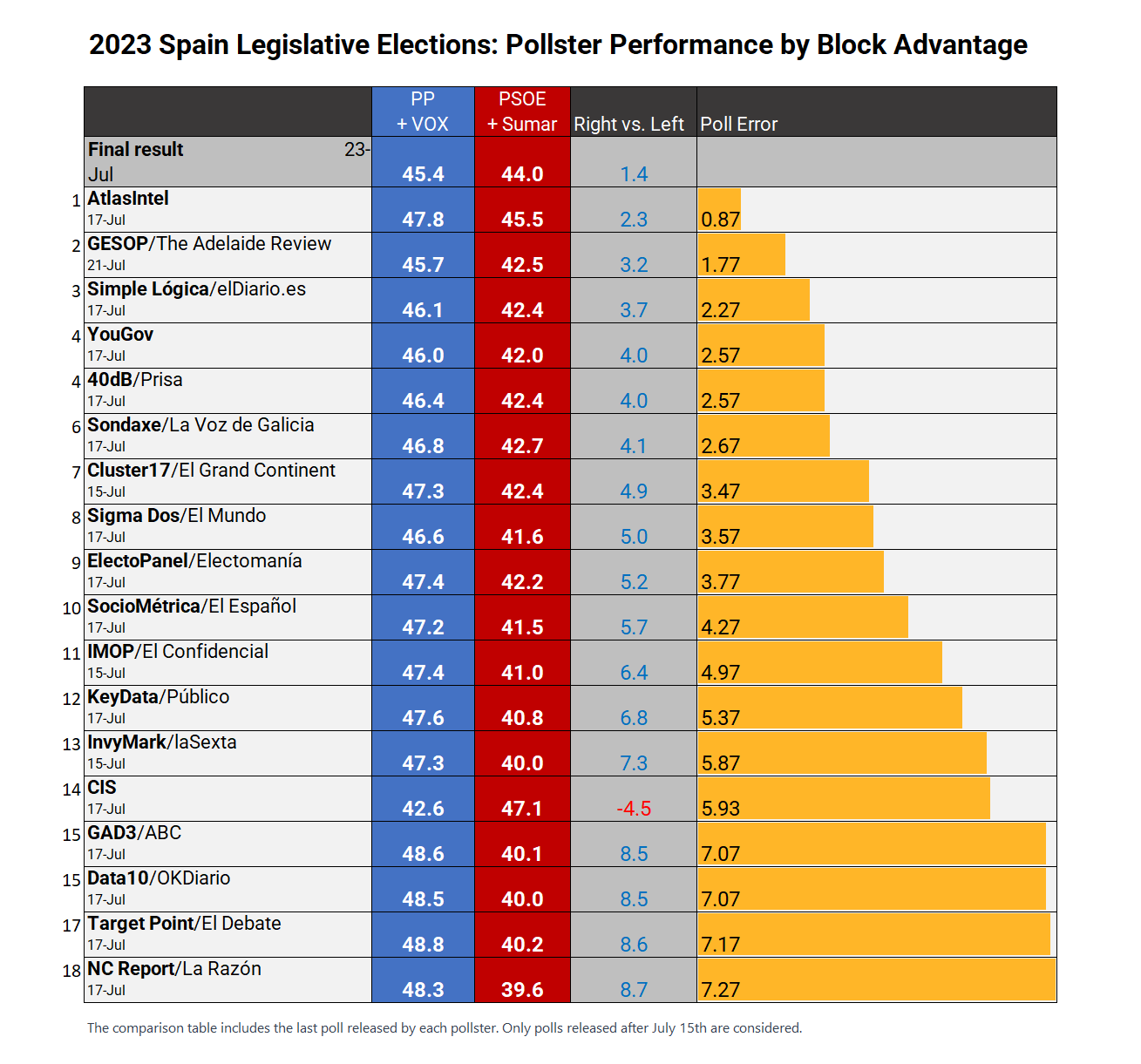
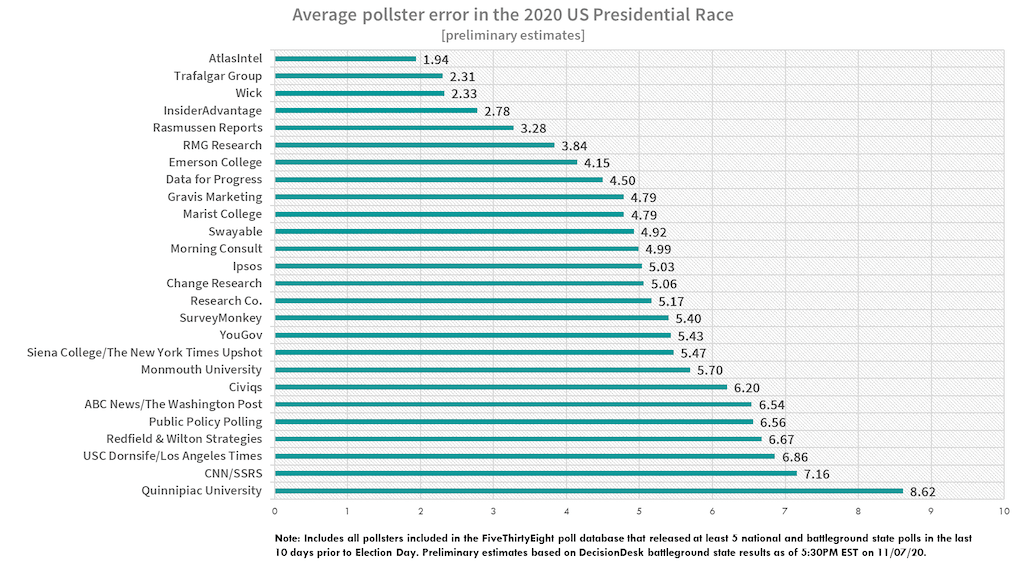
Ever wonder why some polls predict one thing, but reality turns out completely different? Welcome to the wild world of atlas intel polling bias—a place where numbers don't always tell the whole story. In today’s data-driven era, understanding polling bias is more important than ever if you want to make sense of what's really going on.
Picture this: You're scrolling through your feed, and there it is—a flashy headline claiming "70% of people love pineapple on pizza." Sounds legit, right? But wait, how was that number calculated? Who were these "people"? And why does it feel like they skipped over all the pizza purists out there? That, my friends, is the tip of the iceberg when it comes to polling bias.
From election forecasts to consumer surveys, atlas intel polling bias plays a huge role in shaping how we perceive the world. So buckle up because we're diving deep into the nitty-gritty of polling bias, uncovering its secrets, and learning how to spot it before it tricks us again.
Read also:Nothing Happened Zoro A Deeper Dive Into The Myth
Table of Contents
- What Is Polling Bias?
- Types of Polling Bias
- Atlas Intel Polling Bias Explained
- Why Does Polling Bias Matter?
- How Polling Bias Affects Elections
- Spotting Polling Bias in Action
- Tools to Analyze Polls
- Preventing Polling Bias
- Real-World Examples of Polling Bias
- Conclusion: Stay Sharp Out There
What Is Polling Bias?
Let’s get down to basics. Polling bias happens when the results of a survey or poll don’t accurately reflect the views of the entire population being studied. It can creep in at any stage of the polling process—from designing the questions to selecting participants—and it has the power to skew outcomes big time.
Think about it like cooking a recipe. If you accidentally leave out an ingredient or use the wrong measurements, the final dish just won’t taste right. Similarly, if pollsters mess up their methodology, the results they serve up can be way off base.
And here’s the kicker: sometimes polling bias isn’t even intentional. Yeah, you read that right. Even well-meaning researchers can fall into traps that distort the truth. So whether it’s a botched sample size or a poorly worded question, polling bias is something we all need to watch out for.
Common Causes of Polling Bias
There are tons of ways polling bias can sneak into the mix. Here are a few big ones:
- Sampling Error: When the group of people surveyed doesn’t represent the broader population.
- Question Wording: The way questions are phrased can influence how people respond.
- Nonresponse Bias: Happens when certain groups are less likely to participate in a poll.
- Confirmation Bias: Pollsters might subconsciously design studies to confirm their own beliefs.
Types of Polling Bias
Now that we’ve got the basics down, let’s break it down further. There are several types of polling bias, each with its own quirks and tricks. Understanding these categories will help you become a polling pro in no time.
Sampling Bias
This one’s all about who gets picked for the poll. Imagine trying to predict the weather by only checking the forecast in one city. Doesn’t sound too reliable, right? That’s what happens when pollsters rely on a sample that’s not diverse enough to capture the full picture.
Read also:Matt Rife And Kate Beckinsale A Deep Dive Into Their Connection
Question Wording Bias
Words matter—a lot. A simple tweak in phrasing can totally change how people answer. For example, asking “Do you support cleaner air?” sounds a lot different than “Do you oppose industrial growth?” Both questions might be about environmental policies, but the wording makes all the difference.
Atlas Intel Polling Bias Explained
Alright, so what exactly is this atlas intel polling bias thing everyone’s talking about? Simply put, it’s a specific type of polling bias that arises from the tools and technologies used to collect and analyze data. Companies like Atlas Intel specialize in gathering massive amounts of information, but if their methods aren’t spot-on, the results can be misleading.
For instance, imagine a poll that relies heavily on online responses. While convenient, it might miss out on folks who don’t have internet access or aren’t active online. That gap can create a bias that skews the results toward younger, tech-savvy audiences.
Plus, atlas intel polling often involves complex algorithms that crunch numbers in ways that aren’t always transparent. If those algorithms have flaws—or worse, hidden agendas—the results can be downright deceptive.
Why Does Polling Bias Matter?
Here’s the deal: polling bias isn’t just some nerdy academic issue. It has real-world consequences that affect everything from politics to business to everyday life. When polls are biased, decision-makers end up with flawed information, which can lead to bad choices.
In politics, for example, biased polls can give candidates false confidence or discourage voters from showing up to the polls. In marketing, they can steer companies toward strategies that don’t resonate with their actual customers. And in public health, biased surveys might overlook critical groups, leaving them vulnerable.
The Impact on Trust
When people realize polls are biased, it shakes their trust in the entire system. Think back to election cycles where the polls said one thing, but the results said another. That kind of disconnect can leave voters feeling disillusioned and skeptical.
How Polling Bias Affects Elections
Elections are ground zero for polling bias drama. From predicting winners to influencing voter turnout, biased polls can play a starring role in the political theater. Let’s take a closer look at how this happens.
First off, biased polls can create a “bandwagon effect,” where people jump on the side that seems to be winning. On the flip side, they can also cause a “discouragement effect,” where supporters of a trailing candidate decide not to bother voting. Both scenarios can dramatically alter the outcome of an election.
And let’s not forget about media coverage. When polls are biased, journalists who report on them risk spreading misinformation to millions of readers and viewers. It’s a vicious cycle that can spiral out of control if left unchecked.
Spotting Polling Bias in Action
So, how do you know if a poll is biased? Here are a few red flags to watch for:
- Small or unrepresentative sample sizes.
- Leading or loaded question wording.
- Lack of transparency about methodology.
- Results that seem too good (or bad) to be true.
Being a savvy consumer of polling data means asking the right questions and not taking numbers at face value. If something feels fishy, trust your gut and dig deeper.
Tools to Analyze Polls
Luckily, there are some awesome tools out there to help you analyze polls and spot potential biases. Websites like FiveThirtyEight and RealClearPolitics offer detailed breakdowns of polling data, complete with explanations of methodology and margin of error.
For the tech-savvy among us, there are also software programs and apps that can crunch poll numbers and highlight inconsistencies. Just remember, even these tools aren’t foolproof. Always double-check their findings and consider multiple sources before drawing conclusions.
Preventing Polling Bias
While we can’t eliminate polling bias entirely, there are steps pollsters can take to minimize its impact. Here are a few best practices:
- Use random sampling techniques to ensure diversity in the participant pool.
- Carefully craft questions to avoid leading or loaded language.
- Disclose methodology and potential limitations upfront.
- Regularly review and update polling tools to reflect changing demographics.
As consumers, we can do our part by staying informed, questioning assumptions, and demanding transparency from pollsters. Together, we can create a more accurate and trustworthy polling landscape.
Real-World Examples of Polling Bias
To really understand polling bias, sometimes you need to see it in action. Here are a couple of famous examples:
The Dewey Defeats Truman Fiasco
Back in 1948, newspapers famously declared “Dewey Defeats Truman” based on flawed polling data. Turns out, the sample they used was heavily skewed toward phone owners, who at the time were wealthier and more likely to support Dewey. Oops.
Brexit and the Unexpected Outcome
Fast forward to 2016, and we see another classic case of polling bias with Brexit. Many polls predicted a Remain victory, but the Leave campaign ended up winning. Factors like low voter turnout among younger demographics and underestimated enthusiasm for Leave played a big role in the discrepancy.
Conclusion: Stay Sharp Out There
And there you have it, folks—a deep dive into the world of atlas intel polling bias. Whether you’re a political junkie, a business strategist, or just someone trying to make sense of the news, understanding polling bias is a must-have skill in today’s data-driven world.
Remember, not all polls are created equal. Always question the source, scrutinize the methodology, and never rely on a single number to tell the whole story. By staying vigilant and informed, you can navigate the polling maze with confidence.
So, what are you waiting for? Share this article with your friends, drop a comment below, and keep the conversation going. Because when it comes to polling bias, knowledge truly is power.