Let’s dive right into it, folks. The stock market crash is one of those topics that sends shivers down the spine of investors, economists, and historians alike. When was the stock market crash, you ask? Well, buckle up because we’re about to take a deep dive into the most infamous financial meltdowns in history. From the Great Depression to the more recent 2008 crisis, this ain’t just a story—it’s a lesson that affects all of us. So, whether you’re a seasoned investor or just curious about how the markets work, this article’s got you covered.
Now, I know what you’re thinking—why should you care about something that happened decades ago? Well, here’s the thing: history has a funny way of repeating itself. Understanding when the stock market crash occurred and why it happened can help you protect your finances and make smarter decisions. Think of it as a cheat code for financial survival.
In this article, we’ll break it down for you step by step. We’ll explore the most significant crashes, their causes, and the long-term impacts they’ve had on the global economy. But don’t worry, we won’t bore you with dry textbook jargon. This is gonna be a ride full of insights, interesting facts, and actionable advice. Ready? Let’s go!
Read also:Dilbert Comics A Mustread For Every Office Worker Looking To Survive The Madness
Table of Contents
- What is a Stock Market Crash?
- The Great Crash of 1929
- Black Monday (1987)
- The Dot-com Bubble Burst
- The 2008 Financial Crisis
- Common Causes of Stock Market Crashes
- How to Protect Your Investments
- Historical Data and Statistics
- Key Lessons from Stock Market Crashes
- Conclusion: Are We Ready for the Next Crash?
What is a Stock Market Crash?
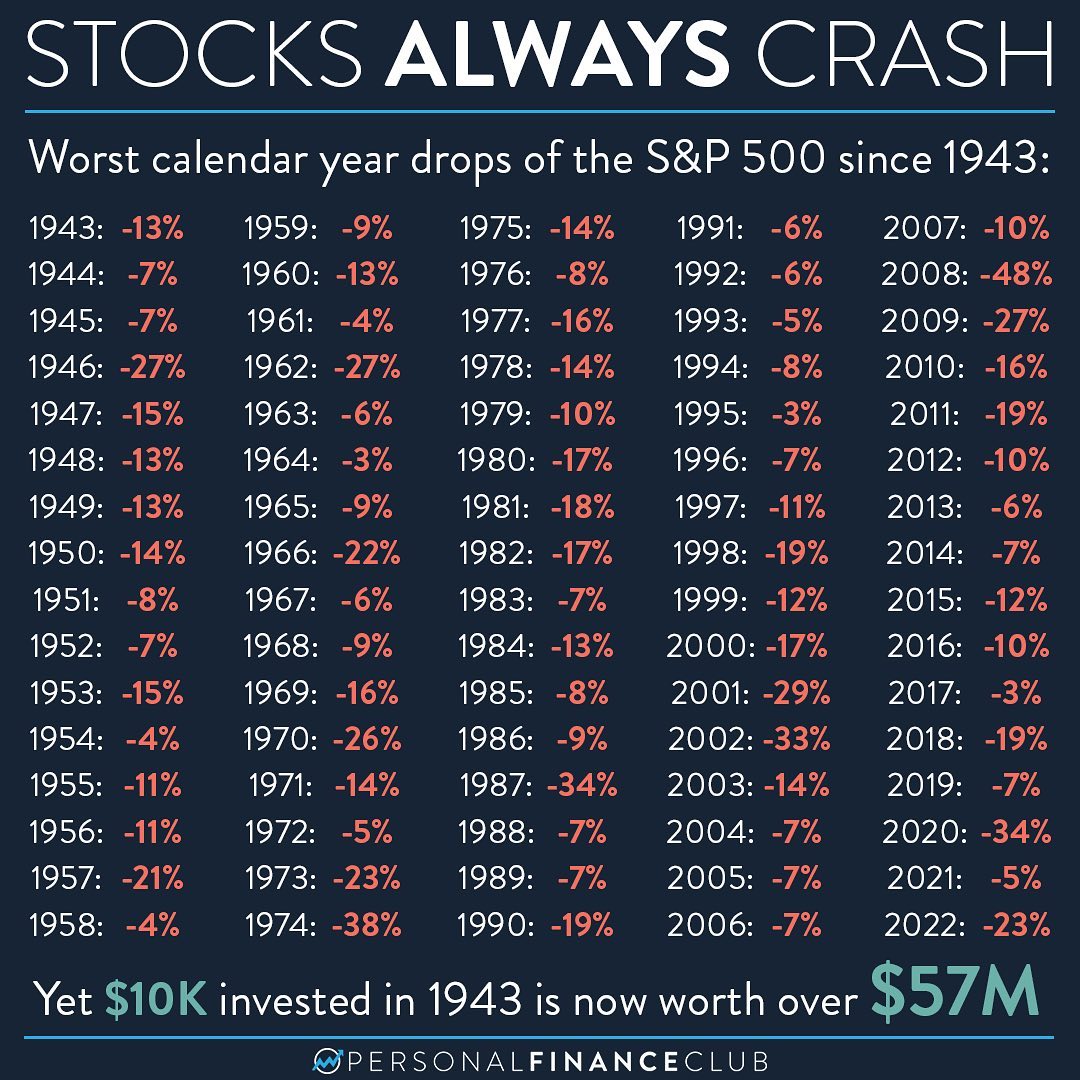
Alright, let’s start with the basics. A stock market crash happens when there’s a sudden and steep drop in stock prices across a significant portion of the market. Imagine a rollercoaster ride gone wrong—except instead of screaming for fun, people are screaming because they just lost their life savings. It’s not a pretty picture, but it’s something that’s happened multiple times throughout history.
Stock market crashes can be triggered by a variety of factors, from economic downturns and speculative bubbles to geopolitical events. They’re often accompanied by panic selling, where investors rush to sell their stocks, causing prices to plummet even further. And let’s not forget the ripple effects on the global economy—recessions, job losses, and financial instability.
Why Should You Care?
Here’s the deal: stock market crashes don’t just affect Wall Street elites. They impact everyday people like you and me. If you’ve got retirement savings, a 401(k), or any investments tied to the stock market, a crash could mean a big hit to your financial future. That’s why understanding these events is crucial for anyone looking to secure their wealth.
The Great Crash of 1929
When was the stock market crash that started it all? The Great Crash of 1929 is often considered the mother of all crashes. It began on October 24, 1929, a day infamously known as “Black Thursday.” By the end of the week, the Dow Jones Industrial Average had dropped by a staggering 25%, sparking the onset of the Great Depression.
What caused it? Well, it was a combination of factors, including excessive speculation, margin buying, and a lack of proper regulation. People were borrowing money left and right to invest in the stock market, thinking prices would keep going up forever. Spoiler alert: they didn’t.
Impact on the Economy
The Great Depression that followed was one of the darkest periods in modern history. Unemployment skyrocketed, banks failed, and millions of people lost their homes and savings. It took over a decade for the economy to recover, and the scars of that crash are still felt today.
Read also:Legolas Lord Of The Rings Actor Unveiling The Enigma Behind The Elven Archer
Black Monday (1987)
Fast forward to October 19, 1987, and we’ve got another infamous crash on our hands. Black Monday, as it’s known, saw the Dow Jones drop by 22.6% in a single day. It was the largest one-day percentage decline in history at the time.
This crash was triggered by a combination of computerized trading, market overvaluation, and geopolitical tensions. Unlike the 1929 crash, however, the economy recovered relatively quickly, thanks to swift action by central banks and regulators.
Lessons Learned
One of the key takeaways from Black Monday was the importance of regulating computerized trading. It also highlighted the need for better risk management practices in the financial industry.
The Dot-com Bubble Burst
Now, let’s talk about the late ’90s and early 2000s. The dot-com bubble was all about the excitement surrounding internet companies. Investors poured money into tech startups, thinking they were the next big thing. Spoiler alert: not all of them were.
When the bubble burst in 2000, the Nasdaq Composite index dropped by over 75%. Companies that had no real business model or revenue stream went belly-up, leaving investors with massive losses.
Why It Happened
The dot-com bubble burst was fueled by excessive optimism and a lack of due diligence. Investors were so caught up in the hype of the internet revolution that they ignored basic financial principles. It was a classic case of speculation gone wrong.
The 2008 Financial Crisis
And then there was the big one—the 2008 financial crisis. This crash was caused by a toxic mix of subprime mortgages, risky lending practices, and a housing market bubble. When the housing market collapsed, it triggered a domino effect that brought down some of the biggest financial institutions in the world.
Lehman Brothers filed for bankruptcy, AIG needed a government bailout, and millions of people lost their homes. It was a financial catastrophe that shook the global economy to its core.
What Were the Long-Term Effects?
The 2008 crisis led to the implementation of stricter financial regulations, such as the Dodd-Frank Act. It also sparked a renewed focus on risk management and transparency in the financial industry. However, the scars of that crisis are still visible today, with many people still skeptical of big banks and Wall Street.
Common Causes of Stock Market Crashes
So, what causes these crashes? While each crash has its own unique set of circumstances, there are some common themes:
- Speculation: When investors get caught up in the hype and start buying assets they don’t fully understand, trouble is bound to follow.
- Overvaluation: When stock prices rise too high too quickly, they become unsustainable and eventually crash back down to earth.
- Lack of Regulation: Without proper oversight, risky financial practices can go unchecked, leading to catastrophic failures.
- Geopolitical Events: Wars, political instability, and other global events can have a significant impact on the markets.
How Can We Prevent Them?
While we can’t completely eliminate the risk of crashes, we can take steps to minimize their impact. This includes implementing stronger regulations, educating investors, and promoting transparency in the financial industry.
How to Protect Your Investments
Now, let’s talk about you. How can you protect your investments from the next crash? Here are a few tips:
- Diversify: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest news and trends in the markets. Knowledge is power, folks.
- Invest for the Long Term: Don’t get caught up in short-term fluctuations. Focus on building wealth over the long haul.
- Work with a Financial Advisor: If you’re not sure where to start, consider working with a professional who can help you navigate the markets.
Historical Data and Statistics
Let’s take a look at some key data points:
- The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell by 25% during the Great Crash of 1929.
- Black Monday in 1987 saw a 22.6% drop in a single day.
- The dot-com bubble burst caused the Nasdaq Composite to drop by over 75%.
- During the 2008 financial crisis, the S&P 500 dropped by nearly 40%.
What Does This Tell Us?
These numbers highlight the volatility of the stock market and the importance of being prepared for the worst. They also show that crashes, while devastating, are often followed by recoveries. It’s a cycle that’s been repeated throughout history.
Key Lessons from Stock Market Crashes
Here are some key lessons we can learn from these crashes:
- Don’t Panic: When the market crashes, the worst thing you can do is panic and sell everything. Stay calm and stick to your long-term strategy.
- Do Your Research: Before investing in anything, make sure you understand what you’re getting into. Don’t rely on hype or speculation.
- Be Prepared for the Worst: Have a contingency plan in place in case the market takes a turn for the worse.
Conclusion: Are We Ready for the Next Crash?
So, there you have it—the history, causes, and lessons of stock market crashes. While we can’t predict the future, we can certainly learn from the past. By understanding what caused these crashes and how they impacted the global economy, we can make smarter decisions and protect our finances.
Are we ready for the next crash? That’s the million-dollar question. While the financial industry has made significant strides in terms of regulation and risk management, there’s always room for improvement. The key is to stay informed, stay diversified, and stay calm.
And hey, don’t forget to share this article with your friends and family. Knowledge is power, and the more people who understand the risks and rewards of the stock market, the better off we’ll all be. So, what are you waiting for? Hit that share button and let’s spread the word!